

RPA vs Traditional Automation: Which One Fits Your Business Needs?






Automation is no longer a futuristic option, it’s a 2025 business necessity. Companies now face a critical choice: RPA (Robotic Process Automation) or traditional automation. While traditional automation has long handled rule-based, structured processes, RPA is rapidly transforming how organizations streamline operations with AI-driven bots and low-code platforms.
According to GlobeNewswire, the global RPA market is projected to reach USD 211.06 billion in 2025, signaling its growing adoption across industries. At the same time, hyperautomation and citizen development are pushing businesses to rethink efficiency models.
This blog explores which automation approach truly fits your business needs using a comparison table highlighting key differences, an overview of challenges and limitations, and step-by-step guidance for successful implementation.
By the end, you’ll gain clarity on whether RPA or traditional automation best aligns with your growth strategy.
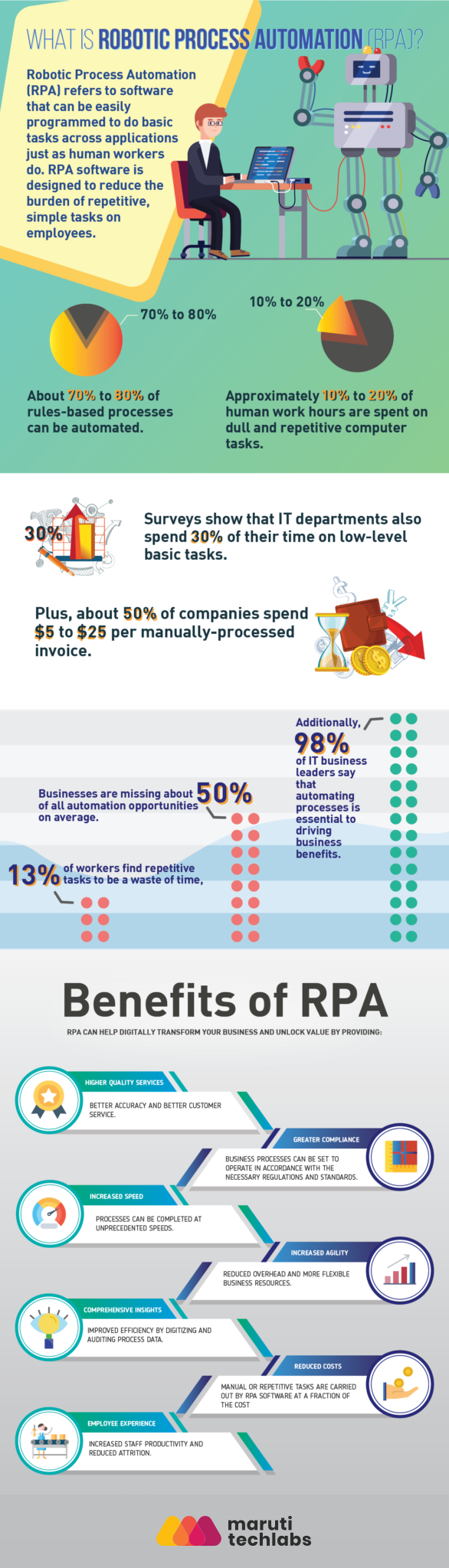
According to IoT Agenda, Robotic process automation (RPA) is the use of software with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) capabilities to handle high-volume, repetitive tasks that typically needed humans to perform.
With RPA, organizations can leverage quick-to-deploy, cost-efficient tools to infuse efficiency and intelligence to their processes- thereby significantly impacting their profits and revenue.
Traditional automation refers to the use of predefined scripts, coding, and system integrations to automate repetitive tasks within IT and business environments. It often requires specialized programming knowledge and is designed for structured, rules-based operations that rarely change. The focus is on efficiency, consistency, and minimizing human intervention in stable processes.
In short, traditional automation excels in stable, complex IT landscapes, making it ideal for enterprises that prioritize system reliability and deep integration over rapid flexibility.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a technology that uses software “bots” to mimic human actions and perform repetitive, rules-based tasks across digital systems. Unlike traditional automation that integrates at the backend, RPA works at the user interface (UI) level, interacting with applications just as a human would clicking buttons, entering data, or extracting information.
This makes it especially effective for automating tasks in environments where backend access or API integration is limited.
In essence, RPA brings speed, flexibility, and cost-efficiency to businesses, empowering them to automate processes at scale while freeing employees to focus on higher-value tasks.
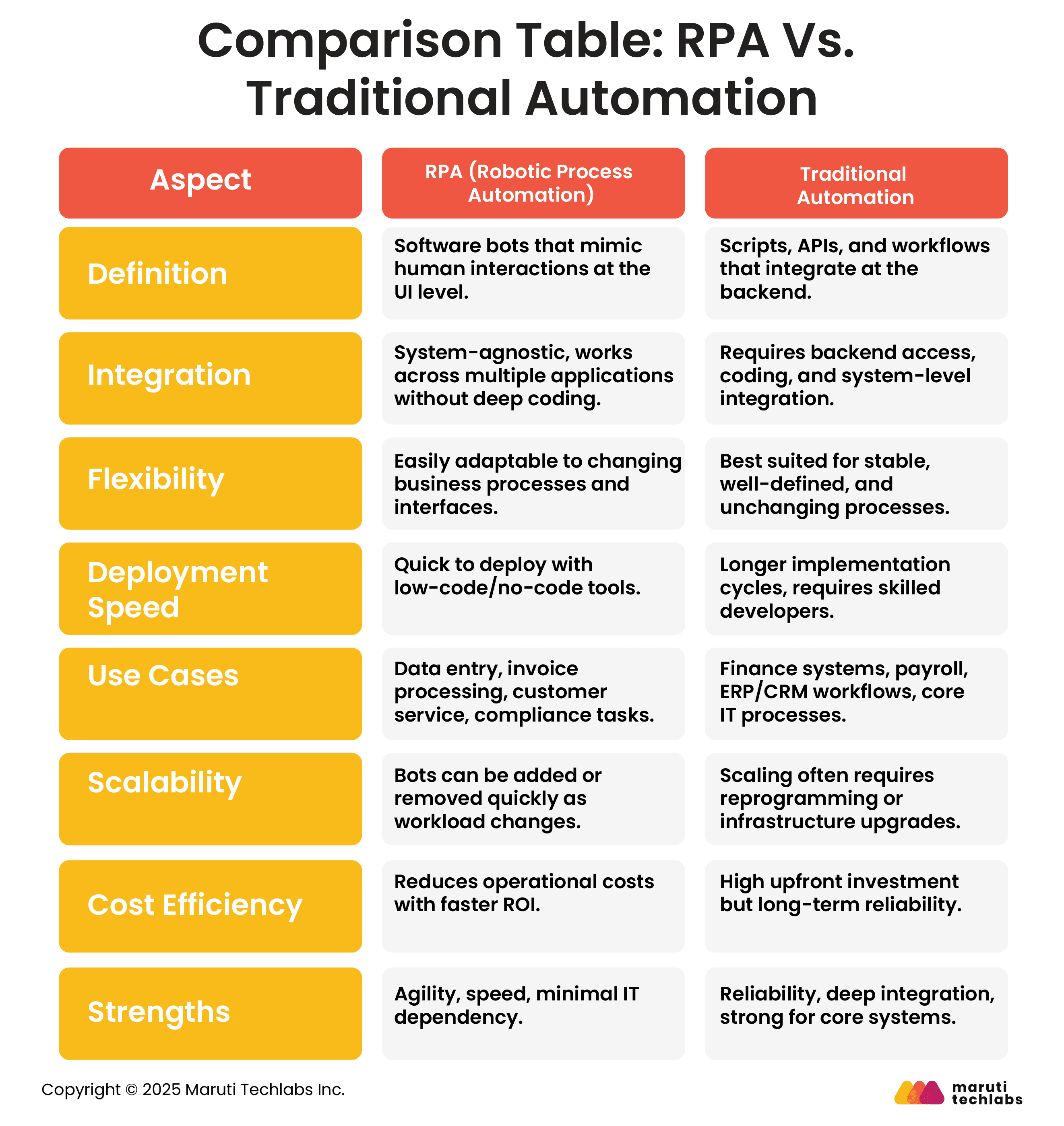
Here’s a comparison table that offers a brief overview of what both processes have to offer.
Here are two real-world examples each of RPA in invoice processing and HR and traditional automation in ERP backend workflows, showcasing how these technologies streamline operations:
Small and medium businesses, in particular, would benefit from the technology as in these businesses, a handful of people handle myriad of issues, including lowering operational costs, bringing new business, retaining existing business, improving workforce productivity, enhancing the quality of products and services, etc.
These businesses are in a better position to reap the following benefits from Robotic Process Automation-
All businesses need an operational boost and want to optimize their processes. Back-end menial tasks hold a considerable chunk of your operational efficiency. Once these tasks are entirely or partly automated, your workforce can focus on the more essential ones, thus, skyrocketing your productivity as an organization.
As processes get streamlined and automated in any business landscape, customer service gets better, and customers feel it in their experience with a business. Robotic Process Automation, when applied strategically to any business, helps expand into higher avenues of efficiency!
According to a report by Forrester, the Enterprise Robotic Process Automation market is expected to reach over $2.9 billion by 2023, while Statista believes the industry will be worth $4.9 billion by just 2021. This massive growth rate of RPA is due to its inexpensive implementation costs and massive ROIs. Consequently, the adoption of the technology will surge.
The potential savings for companies that deploy RPA stand between $5 trillion to $7 trillion, by 2025 (based on studies conducted at Hadoop). Hadoop also estimated that, by 2025, RPA softwares will be performing tasks with an output level that will be equivalent to 140 mn full time employees.
At this rate, it is fairly evident that RPA adoption will be universal in no time. If you happen to be an enterprise looking to streamline and automate processes, the time to act is now.
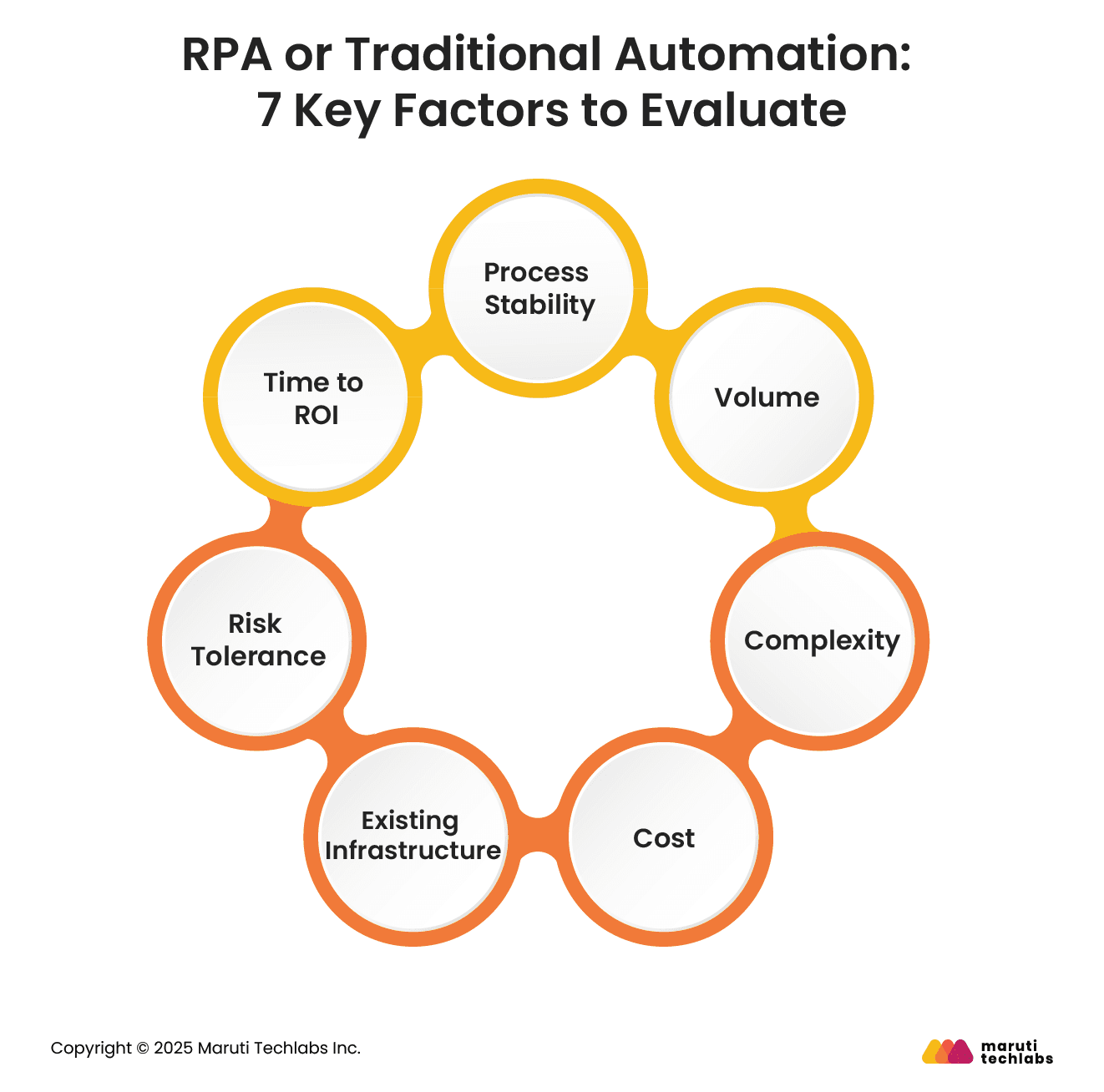
Let’s observe different factors that one must consider before making their to weather opt for RPA or traditional automation.
Let’s learn the risks and challenges associated with employing RPA or traditional automation practices.
Here are 9 steps that you can follow to implement RPA in your business processes.
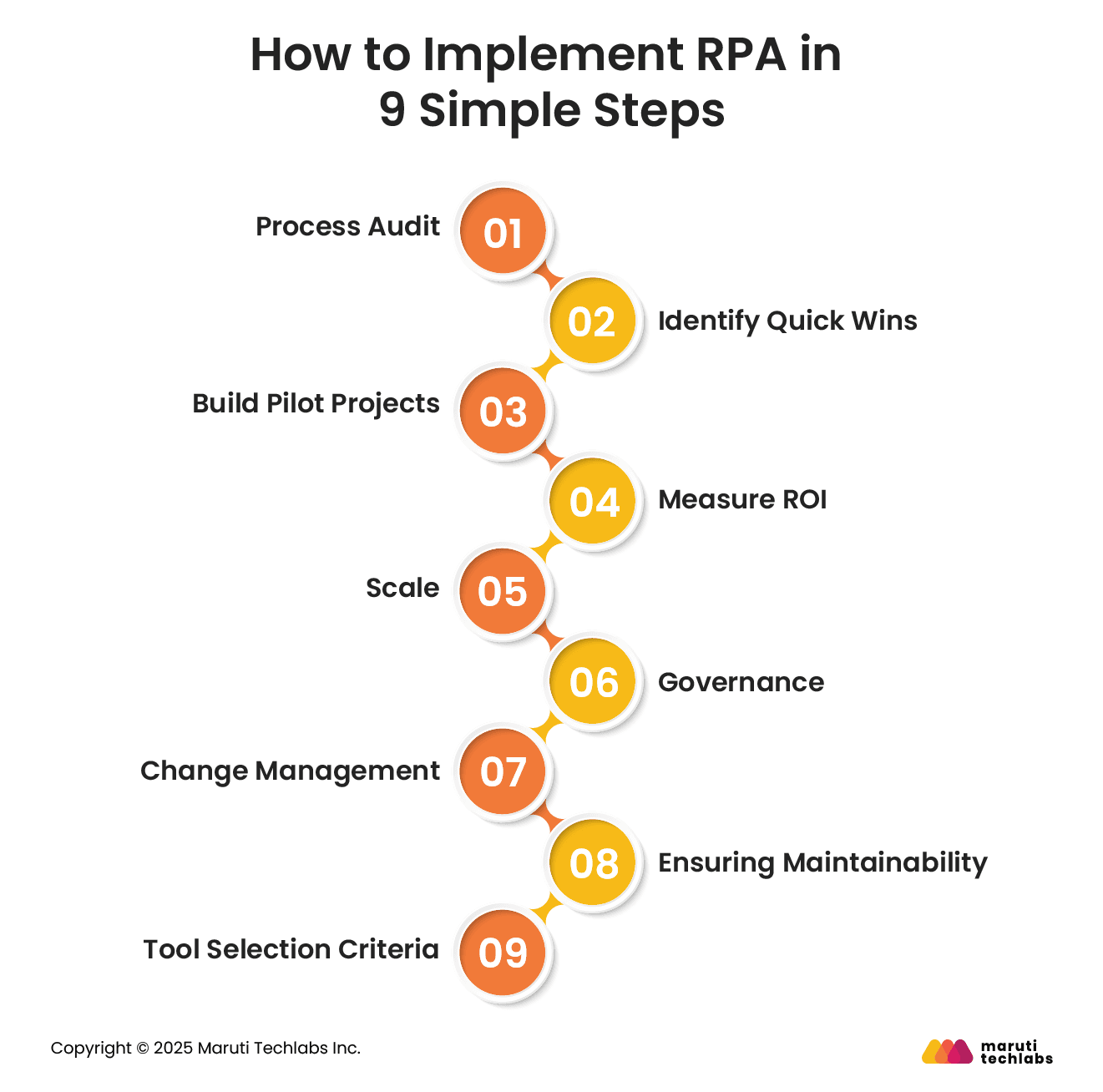
Conduct a thorough audit of current workflows to identify repetitive, rule-based tasks suitable for RPA. Document process inputs, outputs, exceptions, and dependencies. This ensures the automation strategy targets the most impactful areas while avoiding processes that require high human judgment.
Prioritize processes that are easy to automate with high ROI. Quick wins build momentum, justify investment, and demonstrate value. Common candidates include invoice processing, data entry, and report generation, as they are repetitive, high-volume, and deliver immediate efficiency gains.
Develop small-scale pilot RPA projects to validate technology, measure results, and refine workflows. Pilots reduce risk, highlight challenges, and create a blueprint for scaling. They also allow teams to test bot performance in real conditions before full deployment.
Establish clear metrics for RPA success, including cost savings, time reduction, error rate improvement, and employee productivity. Measuring ROI ensures accountability, justifies further investment, and helps refine automation strategies to maximize long-term benefits.
Once pilots prove success, scale RPA across departments and processes. Implement governance, centralized bot management, and orchestration to ensure efficient resource allocation. Prioritize processes with the highest strategic impact to optimize returns while maintaining system stability.
Define governance policies for bot development, deployment, and maintenance. Include access controls, compliance checks, audit trails, and security protocols. Proper governance minimizes risk, ensures consistency, and supports long-term sustainability of RPA initiatives.
Manage organizational change by engaging stakeholders, training employees, and aligning automation goals with business objectives. Effective change management fosters adoption, reduces resistance, and ensures seamless integration of RPA into existing processes.
Design bots for adaptability and ease of maintenance. Use modular designs, proper documentation, and robust exception handling. Regular monitoring and updates ensure bots remain effective despite changes in processes or application interfaces.
Evaluate RPA tools based on scalability, ease of use, integration capabilities, AI/ML features, cost, vendor support, and security. Choosing the right tool aligns technical capabilities with business needs and ensures successful automation deployment.
AI-augmented RPA blends traditional RPA with machine learning and AI, enabling bots to handle more complex processes. Hyper-automation extends automation scope, integrating multiple tools for end-to-end process optimization. This trend boosts efficiency, reduces errors, and allows organizations to automate increasingly dynamic, knowledge-driven tasks beyond repetitive rules.
Large Language Models (LLMs) and AI agents empower RPA to handle unstructured data, complex decision-making, and natural language interactions. These intelligent bots adapt to new scenarios without explicit reprogramming, enabling dynamic process automation such as customer queries, knowledge extraction, and contextual analysis, making automation more intelligent and flexible.
Combining RPA with backend automation through API integration creates hybrid automation models that maximize efficiency. While RPA manages UI-level tasks, backend automation processes data directly within systems. This synergy ensures scalability, reduces bottlenecks, and delivers full value by automating processes end-to-end with speed and robustness.
A lot of work can be automated using RPA in businesses spanning most industries. However, some chunk of these processes may need human intervention for decision making, reasoning, and/or judgment. The task of an RPA engineer, here, would be to assess the complete business process and draw the boundary of RPA, segregating it from the bits where a human would need to act.
Also, RPA cannot deal with exceptional scenarios in the working of a software system. This is another area where an RPA system would require human intervention. But, for everything else, Robotic Process Automation is the key to introducing efficiency into any enterprise.
As a matter of fact, an RPA engineer can look at all these exceptions, create rules within the RPA system and empowering it to handle more and more tasks. In an interview for McKinsey, Leslie Willcocks, professor of work, technology, and globalization at the London School of Economics’ Department of Management, was asked about the several considerations businesses need to make to adopt Robotic Process Automation.
The RPA thought leader outlined the following –
With this, it is fair to conclude that Robotic Process Automation planning is a task in itself. But, how do you differentiate whether an IT solution or a Robotic Process Automation system is the right choice for you?
According to Leslie, it is essential to analyze the process and the need for automation. As companies begin to look carefully, they will find some processes are better implemented with a traditional IT solution, and some others would function better with an RPA solution.
When a quick and easily deployable system is the need of the hour, RPA is the choice to make. It is advisable and desirable to take the IT department onboard sooner rather than later, as they are often in denial of RPA and its benefits.

RPA automates tasks at the user interface level, mimicking human actions without deep system integration. Traditional automation integrates directly into backend systems via scripts, APIs, or workflows, requiring coding. RPA is more flexible, while traditional automation offers deeper integration and is best suited for stable, core business processes.
RPA is generally faster to deploy because it uses low-code/no-code tools and works at the UI level without deep system integration. Traditional automation requires significant development, backend integration, and testing, resulting in longer implementation timelines, especially for complex enterprise processes.
RPA cannot fully replace traditional automation. They serve complementary roles: RPA is ideal for quick, flexible automation of repetitive UI tasks, while traditional automation is better for complex backend workflows requiring deep system integration, stability, and long-term efficiency. Many organizations adopt hybrid models for full value.
RPA has lower upfront costs and faster ROI due to minimal coding and quick deployment, though ongoing bot maintenance adds costs. Traditional automation requires higher initial investment in development, infrastructure, and integration but offers long-term stability and lower ongoing maintenance for stable processes.
RPA risks include UI fragility, frequent maintenance when interfaces change, inability to handle unstructured data without AI integration, scaling challenges, and security vulnerabilities. Proper governance, monitoring, and change management are essential to mitigate these risks effectively.
RPA requires frequent maintenance due to dependency on user interfaces, application changes, and evolving processes. Traditional automation demands less frequent updates but requires deeper technical maintenance for backend integrations, system upgrades, and workflow modifications, often involving significant developer effort.


